Pause In Solar Wind Blows Up Mars’ Atmosphere
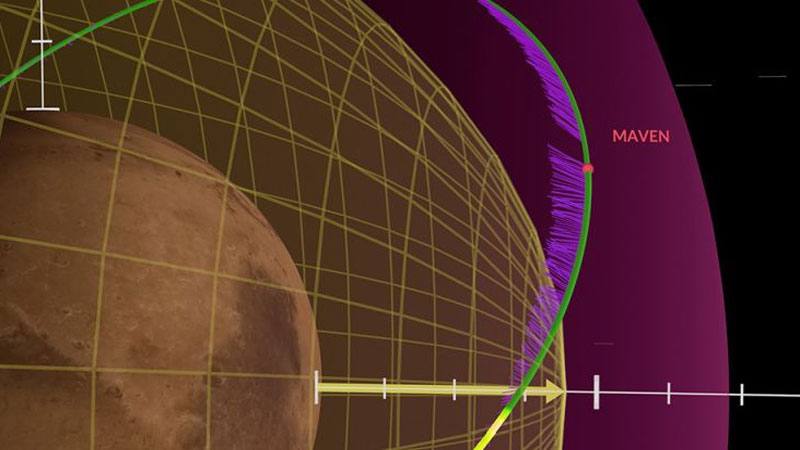
In December 2022, NASA’s MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN) mission orbiting Mars observed an unexpected “disappearance” of the solar wind. The phenomenon is believed to have been caused by a special type of solar event so powerful that it created a vacuum in the flow of charged particles moving through the solar system.
During the observation of electromagnetic phenomena around Mars on December 26, 2022, a 10-fold decrease in solar wind pressure and a 100-fold decrease in the density of its particles were recorded. Analysis of the data showed that at this time the ionosphere and the induced magnetic field of the Red Planet expanded three times. The atmosphere of Mars seemed to have been blown up from within. Obviously, if Mars had been in a system with a less “windy” star, its evolution would have taken a different path.
The Mars experience shows how important it is to take measurements in situ. Without orbital vehicles near near and distant planets, we will not be able to obtain information about processes of this kind. The study of these processes in our system will provide information for modeling atmospheric phenomena around planets in other stellar systems and, in general, will make it possible to better simulate the processes of the origin of life on other worlds.