Apple and Columbia University Develop AI System to Guide Blind Users on the Streets
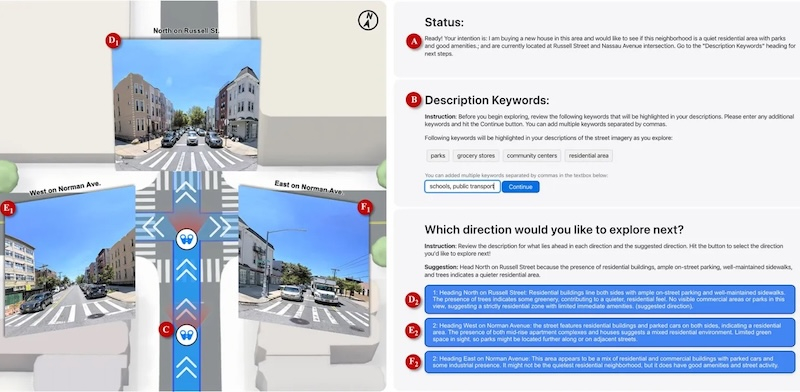
SceneScout is a research project by Apple and Columbia University that aims to help blind and visually impaired people navigate their surroundings. It combines the capabilities of Apple Maps and GPT-4o. Users can not only get turn-by-turn directions and landmarks, but literally explore the entire route block by block.
SceneScout operates in two main modes. Route Preview allows users to see the features of their route in advance, including the condition of sidewalks, the nature of intersections, and the location of bus stops. Virtual Exploration allows users to move freely around the virtual map as they wish, for example to find quiet residential areas or park areas.
Technically, the system is built on the basis of the GPT-4o model, which analyzes panoramic images from Apple Maps and generates structured text descriptions of varying lengths, optimized for screen readers. The interface is specially adapted for working with screen readers.
The study involved 10 blind or visually impaired users, most of whom have experience working with screen readers. They positively assessed the functionality of the system, especially noting the virtual exploration mode, which provides information previously only available to sighted people.
However, it was not without its shortcomings. Some hints contained inaccuracies, such as incorrectly labeled road signs or outdated data on construction work and parked vehicles. It is too early to talk about the implementation of SceneScout. The main goal of the project is to explore the interaction between the Apple Maps API and a multimodal large language model